Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Suzuki, Tomoya*; Otsubo, Ukyo*; Ogata, Takeshi*; Shiwaku, Hideaki; Kobayashi, Toru; Yaita, Tsuyoshi; Matsuoka, Mitsuaki*; Murayama, Norihiro*; Narita, Hirokazu*
Separation and Purification Technology, 308, p.122943_1 - 122943_7, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:24.43(Engineering, Chemical)HNO leaching is used in recycling Pd metal from spent products that primarily contain Ag, and most Pd residues are separated from solutions containing Ag(I). However, a small amount of Pd(II) often remains in these Ag(I) solutions. Therefore, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO
leaching is used in recycling Pd metal from spent products that primarily contain Ag, and most Pd residues are separated from solutions containing Ag(I). However, a small amount of Pd(II) often remains in these Ag(I) solutions. Therefore, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO solutions is essential to promote efficient Pd recycling. In this study, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO
solutions is essential to promote efficient Pd recycling. In this study, the separation of Pd(II) and Ag(I) in HNO solutions was investigated using four N-donor-type adsorbents functionalized with amine (R-Amine), iminodiacetic acid (R-IDA), pyridine (R-Py), or bis-picolylamine (R-BPA). R-Amine, R-IDA, and R-Py selectively adsorbed Pd(II) over Ag(I), Cu(II), Ni(II), and Fe(III) from HNO
solutions was investigated using four N-donor-type adsorbents functionalized with amine (R-Amine), iminodiacetic acid (R-IDA), pyridine (R-Py), or bis-picolylamine (R-BPA). R-Amine, R-IDA, and R-Py selectively adsorbed Pd(II) over Ag(I), Cu(II), Ni(II), and Fe(III) from HNO solutions (0.3-7 M), but R-Amine exhibited a lower Pd adsorption efficiency. In contrast,
solutions (0.3-7 M), but R-Amine exhibited a lower Pd adsorption efficiency. In contrast,  90% of Pd(II), Ag(I), and Cu(II) were adsorbed by R-BPA over the entire range of HNO
90% of Pd(II), Ag(I), and Cu(II) were adsorbed by R-BPA over the entire range of HNO concentrations. Structural analyses of the adsorbed metal ions using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy revealed the separation mechanisms of the N-donor-type adsorbents. Pd(II) adsorption on R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA occurred via Pd(II) coordination of the functional groups (iminodiacetic acid, pyridine, and bis-picolylamine, respectively), whereas that on R-Amine occurred via anion exchange of NO
concentrations. Structural analyses of the adsorbed metal ions using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and extended X-ray absorption fine structure spectroscopy revealed the separation mechanisms of the N-donor-type adsorbents. Pd(II) adsorption on R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA occurred via Pd(II) coordination of the functional groups (iminodiacetic acid, pyridine, and bis-picolylamine, respectively), whereas that on R-Amine occurred via anion exchange of NO
 with [Pd(NO
with [Pd(NO )
) ]
] . The coordinative adsorption mechanisms resulted in the higher Pd(II) adsorption behaviors of R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA. HCl (5.0 M) and thiourea (0.1 M) eluents desorbed 83% of Pd(II) from R-IDA and 95% from R-Py, respectively. R-Py was the most effective Pd(II) adsorbent based on adsorption selectivity and desorption efficiency.
. The coordinative adsorption mechanisms resulted in the higher Pd(II) adsorption behaviors of R-IDA, R-Py, and R-BPA. HCl (5.0 M) and thiourea (0.1 M) eluents desorbed 83% of Pd(II) from R-IDA and 95% from R-Py, respectively. R-Py was the most effective Pd(II) adsorbent based on adsorption selectivity and desorption efficiency.
 Cs NMR chemical shift of clay minerals via machine learning and DFT-GIPAW calculations
Cs NMR chemical shift of clay minerals via machine learning and DFT-GIPAW calculationsOkubo, Takahiro*; Takei, Akihiro*; Tachi, Yukio; Fukatsu, Yuta; Deguchi, Kenzo*; Oki, Shinobu*; Shimizu, Tadashi*
Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 127(4), p.973 - 986, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:56.86(Chemistry, Physical)The identification of adsorption sites of Cs on clay minerals has been studied in the fields of environmental chemistry. The nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) experiments allow direct observations of the local structures of adsorbed Cs. The NMR parameters of  Cs, derived from solid-state NMR experiments, are sensitive to the local neighboring structures of adsorbed Cs. However, determining the Cs positions from NMR data alone is difficult. This paper describes an approach for identifying the expected atomic positions of Cs adsorbed on clay minerals by combining machine learning (ML) with experimentally observed chemical shifts. A linear ridge regression model for ML is constructed from the smooth overlap of atomic positions descriptor and gauge-including projector augmented wave (GIPAW) ab initio data. The
Cs, derived from solid-state NMR experiments, are sensitive to the local neighboring structures of adsorbed Cs. However, determining the Cs positions from NMR data alone is difficult. This paper describes an approach for identifying the expected atomic positions of Cs adsorbed on clay minerals by combining machine learning (ML) with experimentally observed chemical shifts. A linear ridge regression model for ML is constructed from the smooth overlap of atomic positions descriptor and gauge-including projector augmented wave (GIPAW) ab initio data. The  Cs chemical shifts can be instantaneously calculated from the Cs positions on any clay layers using ML. The inverse analysis from the ML model can derive the atomic positions from experimentally observed chemical shifts.
Cs chemical shifts can be instantaneously calculated from the Cs positions on any clay layers using ML. The inverse analysis from the ML model can derive the atomic positions from experimentally observed chemical shifts.
Li, N.*; Sun, Y.*; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Kurosaki, Ken*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 11 Pages, 2023/00
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)During the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear power plant (1F) accident, an overwhelming amount of the cesium remaining in the pressure vessel could have been deposited onto 304 stainless steel (SS304) steam separators and dryers, both with large surface areas. During 1F's decommissioning, the deposited cesium is a safety hazard as it can generate radioactive dust. However, the cohesive and adhesive strengths of CsOH-chemisorbed oxide scales are yet to be defined. In this study, we investigated how CsOH-chemisorption affects the cohesive and adhesive strengths between oxide scales and SS304 substrates with a scratch tester. The scratch test results revealed that the cohesive strengths of the oxide scales decreased after CsOH-chemisorption, while adhesive failure could not be reached.
Saito, Tatsuo; Yamazawa, Hiromi*; Mochizuki, Akihito
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 255, p.107035_1 - 107035_14, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Environmental Sciences)The seasonal variation of dissolved U (DU) in Lake Biwa was reproduced by the following model and parameter research. The introduced models are the water-DU mass balance, and the ion exchange between UO
 and H
and H on the lakeshore soil. The optimized parameters were the CEC of the lakeshore, TU as the sum of DU and AU (soil adsorbed U), kads and kdes as the first order reaction rate coefficients during rapid soil adsorption and desorption of U, respectively. Tabulated by the chemical equilibria constituting DU and analyzed the contribution of each chemical species, it is shown that the seasonal variation of DU is caused by the seasonal variation of pH. A correction to the ion-exchange equilibrium to shift to first order rate reaction only when the daily AU ratio increased above kads or decreased below kdes, improved the reproducibility of DU measurements and reproduced the delay of the DU peak from the pH peak.
on the lakeshore soil. The optimized parameters were the CEC of the lakeshore, TU as the sum of DU and AU (soil adsorbed U), kads and kdes as the first order reaction rate coefficients during rapid soil adsorption and desorption of U, respectively. Tabulated by the chemical equilibria constituting DU and analyzed the contribution of each chemical species, it is shown that the seasonal variation of DU is caused by the seasonal variation of pH. A correction to the ion-exchange equilibrium to shift to first order rate reaction only when the daily AU ratio increased above kads or decreased below kdes, improved the reproducibility of DU measurements and reproduced the delay of the DU peak from the pH peak.
Yakushev, A.*; Lens, L.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J
llmann, Ch. E.*; Khuyagbaatar, J.*; J ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
ger, E.*; Krier, J.*; Runke, J.*; Albers, H. M.*; Asai, Masato; Block, M.*; et al.
Frontiers in Chemistry (Internet), 10, p.976635_1 - 976635_11, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:79.28(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Flerovium (Fl, element 114) is the heaviest element chemically studied so far. The first chemical experiment on Fl suggested that Fl is a noble-gas-like element, while the second studies suggested that Fl has a volatile-metal-like character. To obtain more reliable conclusion, we performed further experimental studies on Fl adsorption behavior on Si oxide and gold surfaces. The present results suggest that Fl is highly volatile and less reactive than the volatile metal, Hg, but has higher reactivity than the noble gas, Rn.
 and Au surfaces in preparation for chemical investigations on Cn, Nh, and Fl at TASCA
and Au surfaces in preparation for chemical investigations on Cn, Nh, and Fl at TASCALens, L.*; Yakushev, A.*; D llmann, Ch. E.*; Asai, Masato; Ballof, J.*; Block, M.*; David, H. M.*; Despotopulos, J.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eberhardt, K.*; et al.
llmann, Ch. E.*; Asai, Masato; Ballof, J.*; Block, M.*; David, H. M.*; Despotopulos, J.*; Di Nitto, A.*; Eberhardt, K.*; et al.
Radiochimica Acta, 106(12), p.949 - 962, 2018/12
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:62.99(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Online gas-solid adsorption studies with single atom quantities of Hg, Tl, and Pb on SiO and Au surfaces were carried out using short-lived radioisotopes with half-lives in the range of 4-49 s. This is a model study to measure adsorption enthalpies of superheavy elements Cn, Nh, and Fl. The short-lived isotopes were produced and separated by the gas-filled recoil separator TASCA at GSI. The products were stopped in He gas, and flushed into gas chromatography columns made of Si detectors whose surfaces were covered by SiO
and Au surfaces were carried out using short-lived radioisotopes with half-lives in the range of 4-49 s. This is a model study to measure adsorption enthalpies of superheavy elements Cn, Nh, and Fl. The short-lived isotopes were produced and separated by the gas-filled recoil separator TASCA at GSI. The products were stopped in He gas, and flushed into gas chromatography columns made of Si detectors whose surfaces were covered by SiO or Au. The short-lived Tl and Pb were successfully measured by the Si detectors with the SiO
or Au. The short-lived Tl and Pb were successfully measured by the Si detectors with the SiO surface at room temperature. On the other hand, the Hg did not adsorb on the SiO
surface at room temperature. On the other hand, the Hg did not adsorb on the SiO surface, but adsorbed on the Au surface. The results demonstrated that the adsorption properties of short-lived Hg, Tl, and Pb could be studied with this setup, and that this method is applicable to the experiment for Cn, Nh, and Fl.
surface, but adsorbed on the Au surface. The results demonstrated that the adsorption properties of short-lived Hg, Tl, and Pb could be studied with this setup, and that this method is applicable to the experiment for Cn, Nh, and Fl.
Matsumura, Taichi; Nagaishi, Ryuji; Katakura, Junichi*; Suzuki, Masahide*
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 192(1), p.70 - 79, 2018/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:11.49(Nuclear Science & Technology)The gamma-scanning of SDS (submerged demineralizer system) vessel used as a typical vessel for decontamination of radioactive water at Three Mile Island Unit 2 (TMI-2) accident was simulated in the axial and radial directions of real and cylindrical-shaped vessels by using a Monte Carlo calculation code (PHITS) on the basis of the geometrical and compositional information of vessel and gamma-scanning available in the previous reports at the accident. In the axial simulation, the true distribution of radioactive  Cs in the zeolite packed bed of vessel was successfully evaluated when a correction function derived from a virtual constant distribution of
Cs in the zeolite packed bed of vessel was successfully evaluated when a correction function derived from a virtual constant distribution of  Cs was applied to the reported gamma-scanning profile. In the radial simulation, the virtual disk-formed and shell-formed sources of
Cs was applied to the reported gamma-scanning profile. In the radial simulation, the virtual disk-formed and shell-formed sources of  Cs displaced in the packed bed were clearly observed from the top and bottom views of vessel. This new radial gamma-scanning indicates that the radial localization of
Cs displaced in the packed bed were clearly observed from the top and bottom views of vessel. This new radial gamma-scanning indicates that the radial localization of  Cs could be well observed by measuring gamma-ray from the top view of vessel during storage. We further examined the radial gamma-scanning from the side view whether the radial localization of
Cs could be well observed by measuring gamma-ray from the top view of vessel during storage. We further examined the radial gamma-scanning from the side view whether the radial localization of  Cs can be confirmed in the normally existing gamma-scanning room or not.
Cs can be confirmed in the normally existing gamma-scanning room or not.
Kumagai, Yuta; Kimura, Atsushi*; Taguchi, Mitsumasa*; Watanabe, Masayuki
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 316(1), p.341 - 348, 2018/04
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:20.93(Chemistry, Analytical)We studied effect of adsorption and condensation by zeolites on radiation-induced degradation of aqueous 2-chlorophenol (2-ClPh). This study aims to demonstrate that the solid-phase extraction using zeolites has potential advantage in treatments of aqueous organic pollutants. Among three zeolites examined in this study, a mordenite type zeolite (HMOR) that has a high Si to Al ratio (127  3) exhibited preferable performance as the matrix for the 2-ClPh degradation. HMOR adsorbed far more 2-ClPh than the other zeolites, which have lower Si/Al ratios. The irradiation of HMOR induced degradation of adsorbed 2-ClPh into Cl
3) exhibited preferable performance as the matrix for the 2-ClPh degradation. HMOR adsorbed far more 2-ClPh than the other zeolites, which have lower Si/Al ratios. The irradiation of HMOR induced degradation of adsorbed 2-ClPh into Cl and organic by-products. We found a significant increase in Cl
and organic by-products. We found a significant increase in Cl production by HMOR. The yield of Cl
production by HMOR. The yield of Cl production in the presence of HMOR was as high as the yield in aqueous solution of 2-ClPh at a concentration 10 times higher. The increased Cl
production in the presence of HMOR was as high as the yield in aqueous solution of 2-ClPh at a concentration 10 times higher. The increased Cl production indicates that the high concentration of adsorbed 2-ClPh led to effective use of the adsorbed energy of HMOR.
production indicates that the high concentration of adsorbed 2-ClPh led to effective use of the adsorbed energy of HMOR.
Takeuchi, Masayuki; Sano, Yuichi; Watanabe, So; Nakahara, Masaumi; Aihara, Haruka; Kofuji, Hirohide; Koizumi, Tsutomu; Mizuno, Tomoyasu
Proceedings of 2017 International Congress on Advances in Nuclear Power Plants (ICAPP 2017) (CD-ROM), 6 Pages, 2017/04
Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao
Photon Factory Activity Report 2016, 2 Pages, 2017/00
In order to elucidate the adsorption states of radioactive Sr-90 in soil, chemical bonding states of non-radioactive strontium adsorbed on layered oxide (mica) have been investigated by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and X-ray absorption near edge structure (XANES) spectroscopy. Since the number of atoms in radioactive Sr-90 is extremely small, the XPS and XANES were measured under total reflection condition of the incident X-rays. The detection limit in total reflection XPS was about 150 pg/cm , which corresponds to 300 Bq of Sr-90. The Sr 2p
, which corresponds to 300 Bq of Sr-90. The Sr 2p core-level energy in XPS shifted to lower energy with the decrease in the thickness of Sr layer. Also, the Sr 2p
core-level energy in XPS shifted to lower energy with the decrease in the thickness of Sr layer. Also, the Sr 2p
 Sr 4d
Sr 4d resonance energy in XANES shifts to lower energy with the decrease in the thickness. On the basis of a simple point charge model, it was elucidated that the chemical bond between Sr and mica surface becomes ionic with the decrease in the adsorbed amount of strontium.
resonance energy in XANES shifts to lower energy with the decrease in the thickness. On the basis of a simple point charge model, it was elucidated that the chemical bond between Sr and mica surface becomes ionic with the decrease in the adsorbed amount of strontium.
Arima, Tatsumi*; Idemitsu, Kazuya*; Inagaki, Yaohiro*; Kawamura, Katsuyuki*; Tachi, Yukio; Yotsuji, Kenji
Progress in Nuclear Energy, 92, p.286 - 297, 2016/09
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:68.36(Nuclear Science & Technology)Diffusion and adsorption behavior of uranyl (UO ) species is important for the performance assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The diffusion behaviors of UO
) species is important for the performance assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The diffusion behaviors of UO , K
, K , CO
, CO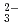 and Cl
and Cl and H
and H O in the aqueous solutions were evaluated by molecular dynamics (MD) calculations. The diffusion coefficient (De) of UO
O in the aqueous solutions were evaluated by molecular dynamics (MD) calculations. The diffusion coefficient (De) of UO is the smallest and is 26% less than the self-diffusion coefficient of H
is the smallest and is 26% less than the self-diffusion coefficient of H O. For the aqueous solution with high concentration of carbonate ions, uranyl carbonate complexes: UO
O. For the aqueous solution with high concentration of carbonate ions, uranyl carbonate complexes: UO CO
CO and UO
and UO (CO
(CO )
) can be observed. For the clay (montmorillonite or illite)-aqueous solution systems, the adsorption and diffusion behaviors of UO
can be observed. For the clay (montmorillonite or illite)-aqueous solution systems, the adsorption and diffusion behaviors of UO and K
and K were evaluated by MD calculations. The distribution coefficients (Kd) increase with the layer charge of clay, and Kd of UO
were evaluated by MD calculations. The distribution coefficients (Kd) increase with the layer charge of clay, and Kd of UO might be smaller than that of K
might be smaller than that of K . Further, their two-dimensional diffusion coefficients were relatively small in the adsorption layer and were extremely small for illite with higher layer charge.
. Further, their two-dimensional diffusion coefficients were relatively small in the adsorption layer and were extremely small for illite with higher layer charge.
Kato, Chiaki; Sato, Tomonori; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Yamagishi, Isao
Proceedings of 17th International Conference on Environmental Degradation of Materials in Nuclear Power Systems - Water Reactors, Vol.2, p.1357 - 1374, 2016/05
With respect to the long-term storage of the zeolite-containing spent Cs adsorption vessels used at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, the corrosion of the vessel material is one of the most important issues. In this study, we performed electrochemical tests on stainless steel specimens in zeolite-containing artificial seawater under gamma-ray irradiation. The spontaneous potential ESP and critical pitting potential VC of the type 316L steel in systems in contact with various zeolites were measured in order to evaluate the corrosion resistance of the steel. In addition, the water sample was analyzed after being irradiated, in order to determine the concentrations of various dissolved oxidants such as oxygen and hydrogen peroxide, which can accelerate the corrosion process. The steady-state rest potential increased with an increase in the dose rate; however, the increase was suppressed in contact with the zeolites. The VC value of the steel when in contact with the zeolites was slightly smaller than the VC value in bulk water; however, the choice of the zeolite used as herschelite, IE96 and IE911 hardly affect the VC value. The concentration of H O
O in the bulk water under irradiation also increased with the increase in the dose rate. This increase was suppressed in the systems in contact with the zeolites, owing to the decomposition of the H
in the bulk water under irradiation also increased with the increase in the dose rate. This increase was suppressed in the systems in contact with the zeolites, owing to the decomposition of the H O
O by the zeolites. A clear relationship was observed between ESP and the H
by the zeolites. A clear relationship was observed between ESP and the H O
O concentration. As contact with the zeolites caused the increase in ESP under irradiation to be suppressed, it can be concluded that the presence of zeolites in the spent Cs adsorption vessels can reduce the probability of the localized corrosion of the stainless steel in the vessels.
concentration. As contact with the zeolites caused the increase in ESP under irradiation to be suppressed, it can be concluded that the presence of zeolites in the spent Cs adsorption vessels can reduce the probability of the localized corrosion of the stainless steel in the vessels.
 at the single-atom level
at the single-atom levelSteinegger, P.*; Asai, Masato; Dressler, R.*; Eichler, R.*; Kaneya, Yusuke*; Mitsukai, Akina*; Nagame, Yuichiro; Piguet, D.*; Sato, Tetsuya; Sch del, M.; et al.
del, M.; et al.
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 120(13), p.7122 - 7132, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:23 Percentile:60.73(Chemistry, Physical)A new experimental method "vacuum chromatography" has been developed to measure adsorption enthalpy of superheavy elements, and its feasibility has been examined using short-lived thallium isotopes. The short-lived thallium isotopes were produced at the JAEA tandem accelerator. The thallium ion beam prepared with an on-line isotope separator which ionized and mass-separated the thallium isotopes was injected into an isothermal vacuum chromatography apparatus. A temperature-dependent adsorption property of thallium atom on SiO surface were measured. The adsorption enthalpy of thallium was determined to be 158 kJ/mol. The thallium is a homolog of element 113. Thus, the vacuum chromatography developed in this study enables us to perform chemical experiments for short-lived superheavy elements with half-lives of a order of one second.
surface were measured. The adsorption enthalpy of thallium was determined to be 158 kJ/mol. The thallium is a homolog of element 113. Thus, the vacuum chromatography developed in this study enables us to perform chemical experiments for short-lived superheavy elements with half-lives of a order of one second.
 and Hg
and Hg metal ions from aqueous medium using Ti(IV) iodovanadate cation exchanger
metal ions from aqueous medium using Ti(IV) iodovanadate cation exchangerNaushad, M.*; Alothman, Z. A.*; Awual, M. R.; Alam, M. M.*; Eldesoky, G. E.*
Ionics, 21(8), p.2237 - 2245, 2015/08
Times Cited Count:273 Percentile:99.62(Chemistry, Physical) -ray irradiation in zeolite/water mixtures
-ray irradiation in zeolite/water mixturesKumagai, Yuta
Hoshasen Kagaku (Internet), (99), p.53 - 56, 2015/04
Radiation-induced degradation of 2-chlorophenol (2-ClPh) in zeolite/water mixtures was studied in order to consider a possibility of adsorption on zeolites to improve efficiencies of irradiation treatments of water contaminated by organic compounds. The degradation of 2-ClPh by  -ray irradiation was investigated as a model compound. The degradation was evaluated by chloride ion (Cl
-ray irradiation was investigated as a model compound. The degradation was evaluated by chloride ion (Cl ) production. A high concentration of Cl
) production. A high concentration of Cl was observed after the irradiation of a mixture with a mordenite-type zeolite (NaMOR), whereas A-type and X-type zeolites showed no significant effect. Therefore, for the mixture with NaMOR, effects of pH of the solution and of the 2-ClPh concentration were examined. At pH 5.7, the excess production of Cl
was observed after the irradiation of a mixture with a mordenite-type zeolite (NaMOR), whereas A-type and X-type zeolites showed no significant effect. Therefore, for the mixture with NaMOR, effects of pH of the solution and of the 2-ClPh concentration were examined. At pH 5.7, the excess production of Cl was induced by the addition of NaMOR. Concurrently, adsorption of 2-ClPh on NaMOR was observed. When the mixture contained a higher concentration of 2-ClPh at pH 5.7, the Cl
was induced by the addition of NaMOR. Concurrently, adsorption of 2-ClPh on NaMOR was observed. When the mixture contained a higher concentration of 2-ClPh at pH 5.7, the Cl production increased. The adsorption of 2-ClPh also increased with increasing concentration. The results suggest that organics adsorbed on zeolites are decomposed by irradiation effectively at high adsorption concentrations.
production increased. The adsorption of 2-ClPh also increased with increasing concentration. The results suggest that organics adsorbed on zeolites are decomposed by irradiation effectively at high adsorption concentrations.
Ueki, Yuji; Saiki, Seiichi; Seko, Noriaki
Nihon Ion Kokan Gakkai-Shi, 25(4), p.99 - 104, 2014/11
Yamada, Hirohisa*; Yokoyama, Shingo*; Watanabe, Yujiro*; Suzuki, Masaya*; Suzuki, Shinichi; Hatta, Tamao*
Nihon Ion Kokan Gakkai-Shi, 25(4), p.207 - 211, 2014/11
 C from irradiated graphite materials, 1; Oxidation behaviors and the changes in pore structure of Q1 and IG-110 graphite due to the air reaction (Joint research)
C from irradiated graphite materials, 1; Oxidation behaviors and the changes in pore structure of Q1 and IG-110 graphite due to the air reaction (Joint research)Fujii, Kimio
JAERI-Tech 2005-048, 108 Pages, 2005/09
The graphite-moderated power reactor was shut down in 1998 and its decommissioning program is being planned. Various graphites are used in the core of magnox-type reactors and HTTR as core-support structural materials and moderating materials of fast neutrons. For the nuclear graphite disposal, it is necessary to determine especially the treatment of long-lived nuclides, such as  C which are generated in the graphite components during reactor operation. As a research, which solves the problem of the
C which are generated in the graphite components during reactor operation. As a research, which solves the problem of the  C concentration, the cooperative research is concluded between JAERI and Japan Nuclear Power Corp. in 1999, and the research for the basic data acquisition has been advanced up to the present. To find the optimum conditions for
C concentration, the cooperative research is concluded between JAERI and Japan Nuclear Power Corp. in 1999, and the research for the basic data acquisition has been advanced up to the present. To find the optimum conditions for  C reduction, basic data on oxidation reaction and the structure of graphite materials are indispensable. In the present experiment, we measure the air oxidation characteristics in the temperature range 450
C reduction, basic data on oxidation reaction and the structure of graphite materials are indispensable. In the present experiment, we measure the air oxidation characteristics in the temperature range 450 800
800 C in Quality1 graphite and IG-110 graphite. Changes in pore diameter and pore size distribution due to air oxidation are discussed.
C in Quality1 graphite and IG-110 graphite. Changes in pore diameter and pore size distribution due to air oxidation are discussed.
Morita, Yasuji; Kubota, Masumitsu*
JAERI-Review 2005-041, 35 Pages, 2005/09
Research and development on Partitioning in JAERI are reviewed in the present report from the beginning to the development of the 4-Group Partitioning Process and its test with real high-level liquid waste (HLLW). In the 3-Group Partitioning Process established in around 1980, elements in HLLW are separated into 3 groups of transuranium element group, Sr-Cs group and the other element group. The 4-Group Partitioning Process subsequently developed contains the separation of Tc-platinum group metals additionally. The process was tested to demonstrate its performance with real concentrated HLLW. Until then, various separation methods for various elements were studied and selection and optimization of the separation methods were carried out to establish the process. Review of the experience, findings and results is very important and valuable for future study on partitioning. The present report is prepared from this point of view.
Takakuwa, Yuji*; Ogawa, Shuichi*; Ishizuka, Shinji*; Yoshigoe, Akitaka; Teraoka, Yuden
Shokubai, 47(5), p.352 - 357, 2005/08
Oxidation reactions of Ti(0001) surfaces were monitored by real-time photoelectron spectroscopy with high brilliant synchrotron radiation and He-I resonance line. An oxygen adsorption model and ultra-thin oxide layers formation processes were reviewed on the basis of time evolutions of the adsorbed oxygen amount, oxidation states, electronic states and the work function, which were obtained from photoelectron spectra for Ti 2p and O 1s core levels as well as the valence band.